blood test for diabetes insipidus Diabetes test blood ucla launches campuswide initiative prevention
Living with diabetes insipidus can be challenging, but with proper management and support, you can lead a fulfilling life. This rare condition affects the body’s ability to regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive thirst and frequent urination. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you navigate this condition with confidence and take control of your health.
What is Diabetes Insipidus?
Diabetes insipidus is a disorder that affects the kidneys’ ability to conserve water. Unlike diabetes mellitus, which affects blood sugar control, diabetes insipidus is characterized by excessive thirst and the production of large amounts of diluted urine. This condition occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or when the kidneys are unable to respond to it.
 It is important to recognize the symptoms of diabetes insipidus, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications. Some common symptoms include:
It is important to recognize the symptoms of diabetes insipidus, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications. Some common symptoms include:
- Intense thirst (polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Waking up multiple times at night to urinate
- Dehydration
- Weakness and fatigue
Types and Causes of Diabetes Insipidus
There are different types of diabetes insipidus, each with its own causes:
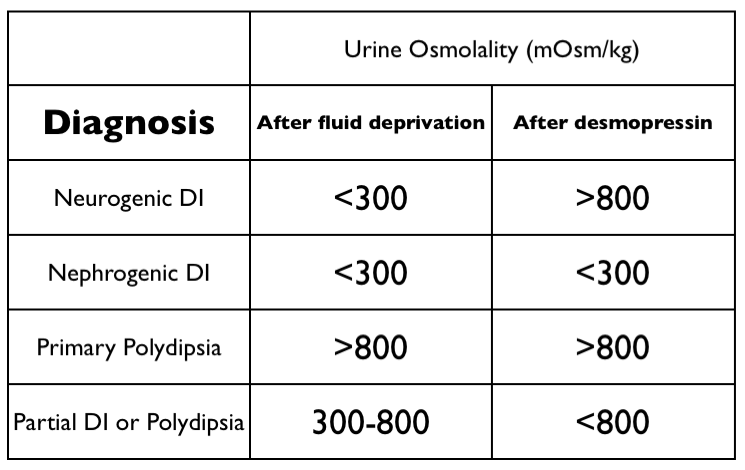
- Central diabetes insipidus (CDI): This type occurs when there is a problem with the production or release of ADH from the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. It can be caused by head trauma, tumors, genetic disorders, or certain medications.
- Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI): NDI occurs when the kidneys are unable to respond to ADH. This can be caused by genetic mutations, kidney disease, or certain medications.
- Gestational diabetes insipidus: This type of diabetes insipidus occurs during pregnancy due to an increase in placental production of a substance that inhibits ADH.
- Dipsogenic diabetes insipidus: This rare type is caused by a defect in the thirst mechanism, leading to excessive fluid intake and dilution of urine.
Treatment Options for Diabetes Insipidus
Treatment for diabetes insipidus aims to relieve symptoms, maintain fluid balance, and prevent dehydration. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type and underlying cause of the condition.
 Common treatment options include:
Common treatment options include:
- Desmopressin: This synthetic analog of ADH can be taken as a nasal spray, oral tablet, or injection to replace or supplement the missing hormone.
- Hydrochlorothiazide: This medication can help the kidneys to concentrate urine, reducing excessive urination.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Indomethacin, in particular, can help reduce urine production in some cases of NDI.
- Lifestyle modifications: Managing fluid intake and frequently monitoring urine output can help maintain fluid balance. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate daily fluid intake.
Living with diabetes insipidus requires careful management and regular monitoring of fluid balance. It is important to raise awareness about this condition and support others who may be going through similar challenges. By sharing information and personal experiences, we can create a supportive community that empowers individuals with diabetes insipidus to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
If you are looking for UCLA launches campuswide diabetes prevention initiative | UCLA you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about UCLA launches campuswide diabetes prevention initiative | UCLA like UCLA launches campuswide diabetes prevention initiative | UCLA, DIABETES INSIPIDUS, DIABETES YANG BERHUBUNGAN DENGAN GINJAL DAN OTAK and also Diabetes Insipidus Affect Sodium Levels. Read more:
UCLA Launches Campuswide Diabetes Prevention Initiative | UCLA
 newsroom.ucla.edudiabetes test blood ucla launches campuswide initiative prevention
newsroom.ucla.edudiabetes test blood ucla launches campuswide initiative prevention
Diabetes Insipidus Affect Sodium Levels
 joycehorton737headline.blogspot.comEdgar V. Lerma 🇵🇭 On Twitter: “Differentiating Polydipsia, Central
joycehorton737headline.blogspot.comEdgar V. Lerma 🇵🇭 On Twitter: “Differentiating Polydipsia, Central
 twitter.comDIABETES INSIPIDUS, DIABETES YANG BERHUBUNGAN DENGAN GINJAL DAN OTAK
twitter.comDIABETES INSIPIDUS, DIABETES YANG BERHUBUNGAN DENGAN GINJAL DAN OTAK
 dzakiyaharigoh.blogspot.comdiabetes insipidus siadh adh mnemonics endocrino deficiency hormonas ddavp lack insipid kencing fisiopatologia sodium glucose mellitus desmopressin hyposecretion rn ginjal
dzakiyaharigoh.blogspot.comdiabetes insipidus siadh adh mnemonics endocrino deficiency hormonas ddavp lack insipid kencing fisiopatologia sodium glucose mellitus desmopressin hyposecretion rn ginjal
Diabetes Insipidus | The BMJ
 www.bmj.comdiabetes insipidus polydipsia biochemical fig bmj polyuria assessment
www.bmj.comdiabetes insipidus polydipsia biochemical fig bmj polyuria assessment
Diabetes insipidus. Ucla launches campuswide diabetes prevention initiative. Diabetes insipidus polydipsia biochemical fig bmj polyuria assessment